Research and Publications
Publications
Adaptive Obstacle-Aware Task Assignment and Planning for Heterogeneous Robot Teaming
Multi-Agent Task Assignment and Planning (MATP) has attracted growing attention but remains challenging in terms of scalability, spatial reasoning, and adaptability in obstacle-rich environments. To address these challenges, we propose OATH — Adaptive Obstacle-Aware Task Assignment and Planning for Heterogeneous Robot Teaming — which advances MATP by introducing a novel obstacle-aware strategy for task assignment. First, we develop an adaptive Halton sequence map, the first known application of Halton sampling with obstacleaware adaptation in MATP, which adjusts sampling density based on obstacle distribution. Second, we propose a cluster–auction–selection framework that integrates obstacle-aware clustering with weighted auctions and intra-cluster task selection. These mechanisms jointly enable effective coordination among heterogeneous robots while maintaining scalability and nearoptimal allocation performance. In addition, our framework leverages an LLM to interpret human instructions and directly guide the planner in real time. We validate OATH in NVIDIA Isaac Sim, showing substantial improvements in task assignment quality, scalability, adaptability to dynamic changes, and overall execution performance compared to state-of-the-art MATP baselines.
A Hierarchically Integrated Framework for Resilient Task Allocation and Planning in Heterogeneous Multi-Robot Systems
Traditional methods for task allocation and planning in multi-robot teams are typically offline, assuming that all tasks are known in advance and assigned before mission execution. However, real-world environments require resilient planning algorithms capable of handling unexpected scenarios such as task failures, unstructured environments, robot failures, and low battery levels. To address these challenges, we propose a resilient task allocation and planning framework tailored for heterogeneous multi-robot systems, specifically incorporating drones and ground robots such as Turtlebots. The framework combines a high-level task allocation and planning module with a mid-level behavior tree architecture to manage unexpected events during execution. The task allocation problem involves assigning different types of tasks to a heterogeneous robot team, where each robot has specific capabilities suited to certain tasks. The environment includes both known and unknown elements, such as static and dynamic obstacles, adding uncertainty to planning and execution. The goal is to improve resilience to unexpected situations while keeping mission time short. A video has been prepared to present our algorithm, supplementary technical details, and preliminary experimental results.
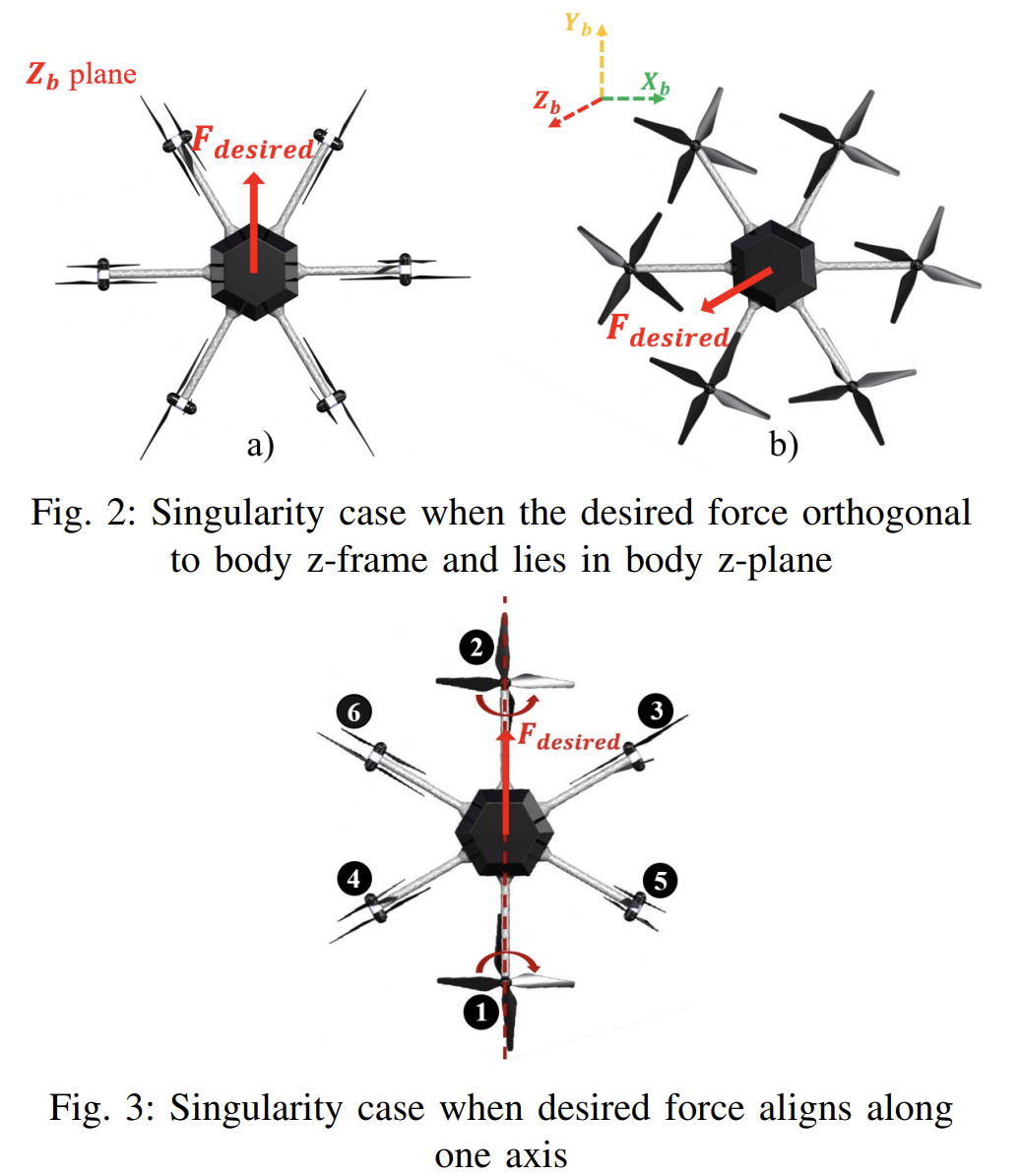
Singularity Free Dynamic Control Allocation for Tilt-rotor Multirotor UAVs
Tilt-rotor multirotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) provide flexible flight capability and pose-omnidirectionality. Although numerous control allocation algorithms have been presented with relatively good reliability, some singularity configurations of tilt-rotor UAVs can cause the algorithm to fail in generating a stable solution. This paper proposes a singularity-free dynamic control allocation algorithm that improves the stability of tilt-rotor multirotor UAVs in 6 degrees of freedom (DOFs). The control allocation is formulated as a constrained optimization problem by introducing inequality constraints derived from singular configurations. A barrier function is embedded into the objective function for constraints enforcement. The Lagrange function is then used to form the unconstrained optimization objective function. A Lyapunov-like function is proven to be negative semidefinite, time invariant and bounded. Through Barbalat’s lemma, the algorithm is uniformly globally stable. Simulation results obtained from trajectory tracking at singularities of the tilt-rotor multirotor UAVs in 6 DOFs demonstrate the validity of the proposed dynamic control allocation approach.
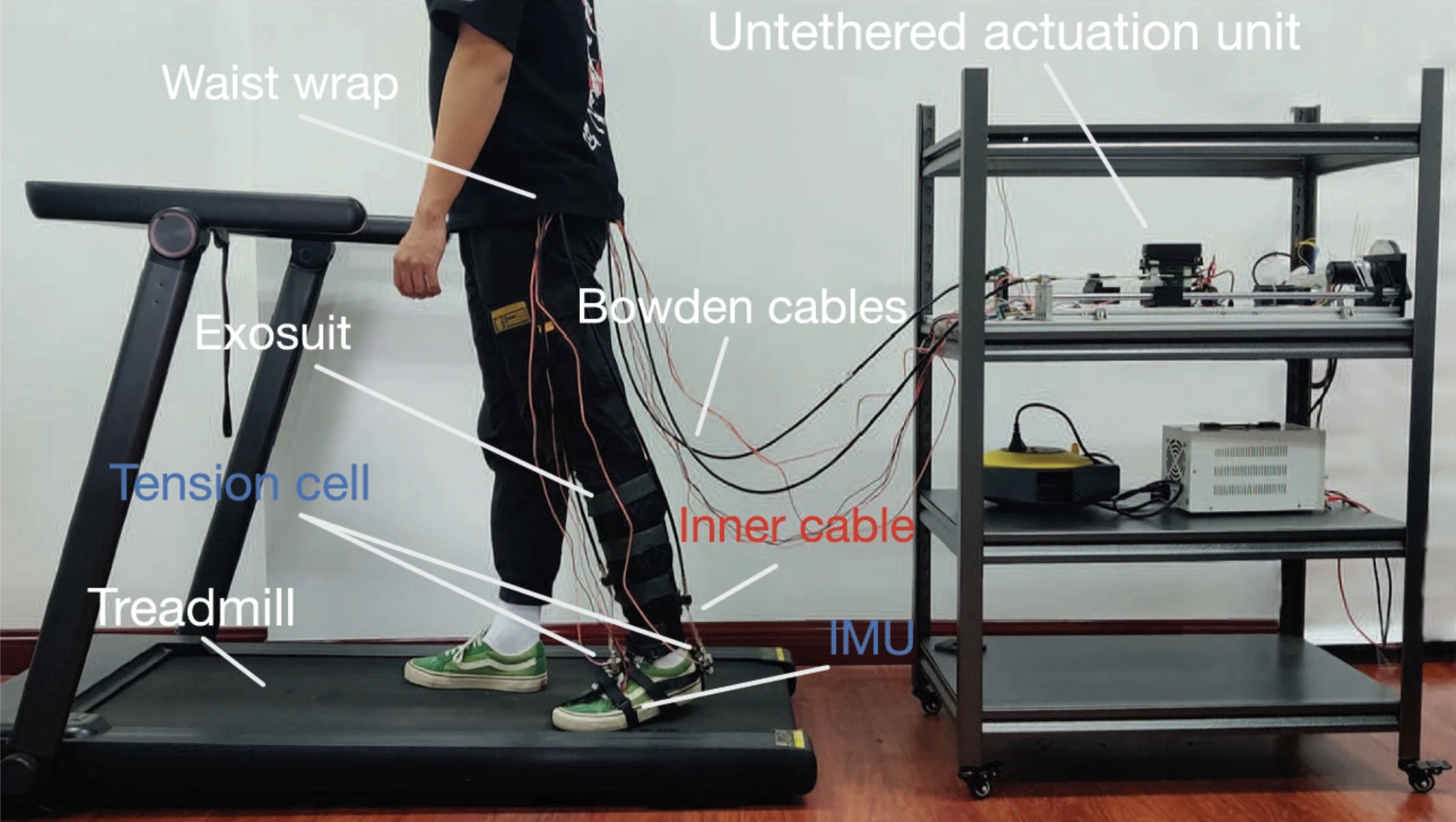
A Segmented Dynamic Movement Primitives-Based Gait Assistive Strategy for Soft Ankle Exosuit
The soft exosuit has been proven to improve the pilot’s walking ability and reduce metabolic consumption, yet its gait assistance strategy still suffers from insufficient personalized adaptation. This paper proposes a Segmented Dynamic Movement Primitives (SDMPs)-based gait assistive strategy. A gait detection algorithm divides a complete gait cycle into four segments, and independent DMPs learn each segment. The normal gait trajectory is referenced and the personalized gait is generated with the spatial-temporal parameters of each DMP automatically adjusted according to sensor data. Experimental results show that the gait of SDMPs is superior to those generated by the traditional method and vanilla DMPs. Force feedback indicates that the gait generated using SDMPs can quickly pull the joint to the desired position in the plantar flexion phase and then quickly complete tension release, which is better than other methods. This method can serve as a new personalized gait assistance strategy for soft ankle exosuits.
Robotics Hardware & Demos
SLAM — TurtleBot Mapping & Goal Navigation
Using TurtleBot to explore an unknown environment and build a map. Tuned navigation parameters for smooth motion, and executed multi-goal navigation to three target waypoints while avoiding obstacles.
Multi-Modal Sensing & Navigation — Vision + LiDAR
CNN and OpenCV detect traffic signals for turn/stop decisions; LiDAR wall-following maintains safe clearance and prevents collisions in narrow corridors.
Skills
Programming
Robotics / Autonomy
ML / Perception
Modeling & Tools
